Observability¶
Introduction¶
Observability feature uses OVN sampling functionality to generate samples with requested metadata when
specific OVS flows are matched. To see the generated samples, a binary called ovnkube-observ is used.
This binary allows printing the samples to stdout or writing them to a file.
Currently, supports observability for:
- Network Policy
- (Baseline) Admin Network Policy
- Egress firewall
- UDN isolation
- Multicast ACLs
More features are planned to be added in the future.
Motivation¶
Networking observability is an important feature to verify the expected networking behavior in a cluster and to debug existing problems. Ovn-kubernetes makes use of many abstraction layers (through NBDB, logical flows, openflow flows and datapath flows) that translate kubernetes feature into very specific rules that apply to each packet in the network. Therefore, even though there are ways to see what OVS/OVN is doing with a particular packet, there is no way to know why.
We aim to solve this problem by providing a way for ovn-kubernetes to generate packet samples enriched with metadata that can be easily correlated back to kubernetes objects or other human-readable pieces of information that provide insights of what ovn-kubernetes is doing with a packet and why.
User-Stories/Use-Cases¶
- As a user I want to make sure that the network policies/egress firewalls/etc. are correctly enforced in my cluster.
- As a cluster admin I want to check why some traffic is allowed or dropped.
How to enable this feature on an OVN-Kubernetes cluster?¶
To enable this feature, use --observability flag with kind.sh script or --enable-observability flag with ovnkube binary.
To see the samples, use ovnkube-observ binary, with -h to see allowed flags. ovnkube-observ is installed on the ovnkube pods. For example:
kubectl -n ovn-kubernetes exec -it <ovnkube pod> -c ovnkube-controller -- ovnkube-observ -h
Usage of ovnkube-observ:
-add-ovs-collector
Add ovs collector to enable sampling. Use with caution. Make sure no one else is using observability.
-enable-enrichment
Enrich samples with nbdb data. (default true)
-filter-dst-ip string
Filter in only packets to a given destination ip.
-filter-src-ip string
Filter in only packets from a given source ip.
-log-cookie
Print raw sample cookie with psample group_id.
-output-file string
Output file to write the samples to.
-print-full-packet
Print full received packet. When false, only src and dst ips are printed with every sample.
This feature requires OVS 3.4 and linux kernel 6.11.
Workflow Description¶
- Observability is enabled by setting the
--enable-observabilityflag in theovnkubebinary. - For now all mentioned features are enabled by this flag at the same time.
- To start observing and display the samples, run
ovnkube-observ -add-ovs-collector. Samples are only generated when the real traffic matching the ACLs is sent through the OVS. An example output is:
OVN-K message: Allowed by default allow from local node policy, direction ingress
src=10.129.2.2, dst=10.129.2.5
Support in observability tools¶
- NetObserv: through the
NetworkEventsagent feature.
Implementation Details¶
User facing API Changes¶
No API changes were done.
OVN sampling details¶
OVN has 3 main db tables that are used for sampling:
- Sample_collector: This table is used to define the sampling collector. It defines the sampling rate via Probability field
and collectorID via SetID field, which is used to set up collectors in the OVS.
- Sampling_app: This table is used to set IDs for existing OVN sampling applications, that are sent together with the samples.
There is a supported set of Sampling_app types, for example acl-new app is used to sample new connections matched by an ACL.
Sampling_app.ID is a way to identify the application that generated the sample.
- Sample: This table is used to define required samples and point to the collectors.
Every sample has Metadata that is sent together with the sample.
Samples are attached to the other db tables, for now only to ACLs.
A sample is generated when a packet matches the ACL. Every Sample contains Sampling_app.ID and Sample.Metadata,
that is decoded by go-controller/observability-lib.
OVN-Kubernetes Implementation Details¶
Sample_collector and Sampling_app are created or cleaned up when the observability is enabled/disabled on startup.
When one of the supported objects (for example, network policy) is created, ovn-kuberentes generates an nbdb Sample for it.
To decode the samples into human-readable information, go-controller/observability-lib is used. It finds Sample
by the attached Sample.Metadata and then gets corresponding db object (e.g. ACL) based on Sampling_app.ID and Sample.UUID.
The message is then constructed using db object (e.g. ACL) external_ids.
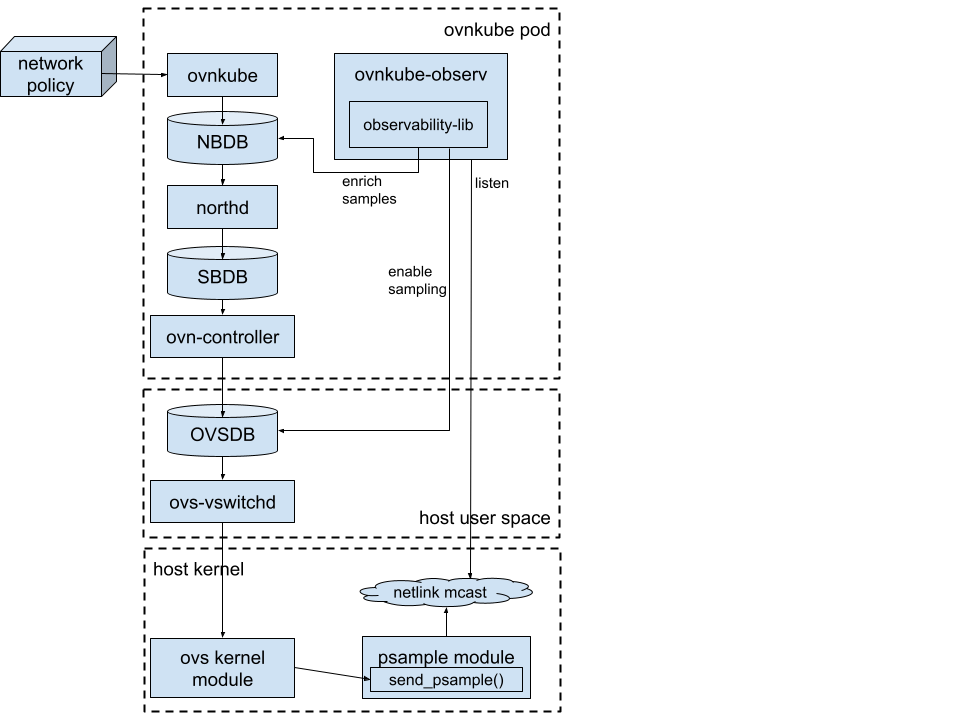
The diagram shows how all involved components (kernel, OVS, OVN, ovn-kubernetes) are connected.
Enabling collectors¶
Currently, we have only 1 default collector with hard-coded ID, which is set via the Sample_collector.SetID field.
To make OVS start sending samples for an existing Sample_collector, a new OVSDB Flow_Sample_Collector_Set entry
needs to be created with Flow_Sample_Collector_Set.ID value of Sample_collector.SetID.
This is done by the go-controller/observability-lib and it is important to note that only one Flow_Sample_Collector_Set
should be created for a given Sample_collector.SetID value at a time. But if such entry already exists, it can be reused.
Best Practices¶
TDB
Future Items¶
Add more features support, for example, egress IP or load balancing.
Known Limitations¶
Current version of ovnkube-observ only works in OVN-IC mode, as it requires nbdb to be available locally via unix socket.
In the future non-IC will also be supported with provided nbdb address and certificates.
Only default network observability is supported for now, secondary-network observability will be added later.
Sample ID for ACL is stored in conntrack when the new session is established and is never updated until the session is closed. That means, some samples may be removed from nbdb, but still be present in the generated samples. It implies: - ACL-based sampling only affects newly established connections: if a session was already established before the sampling was enabled, the session will not be sampled. - If a session is established with enabled sampling, disabling sampling won't affect that session, and it will continue generating samples until the session is closed. - If the sample was removed from nbdb (e.g. when sampling is disabled for a given connection or when ACL is updated on network policy update or delete) generated samples won't be decoded, as required data is not present in nbdb anymore.
Due to OVN limitations, some samples can only be generated on the first packet of a connection. This applies to - egress firewall, as it doesn't submit a flow to conntrack. - multiple ACLs on the same direction, as only last-tier ACL will be submitted to conntrack. For now this applies to - ANP + network policy - ANP + BANP
in both cases ANP will have only first-packet sample.
Use caution when running the ovnkube-observe tool. Currently it has poor resource management and consumes a lot of
CPU when many packets are sent. Tracked here https://github.com/ovn-kubernetes/ovn-kubernetes/issues/5203
References¶
NONE