OVN-Kubernetes Network Topology¶
Like we saw earlier in the architecture section there are two modes of deployment in OVN-Kubernetes:
- central mode (centralized control plane architecture) -- deprecated starting 1.2 release
- interconnect mode (distributed control plane architecture) -- default mode
Based on the mode, there are subtle differences in network topology running on each node in the cluster
OVN-Kubernetes Network Topology - Central Mode (DEPRECATED!!!)¶
The centralized architecture in OVN-K looks like this today:
+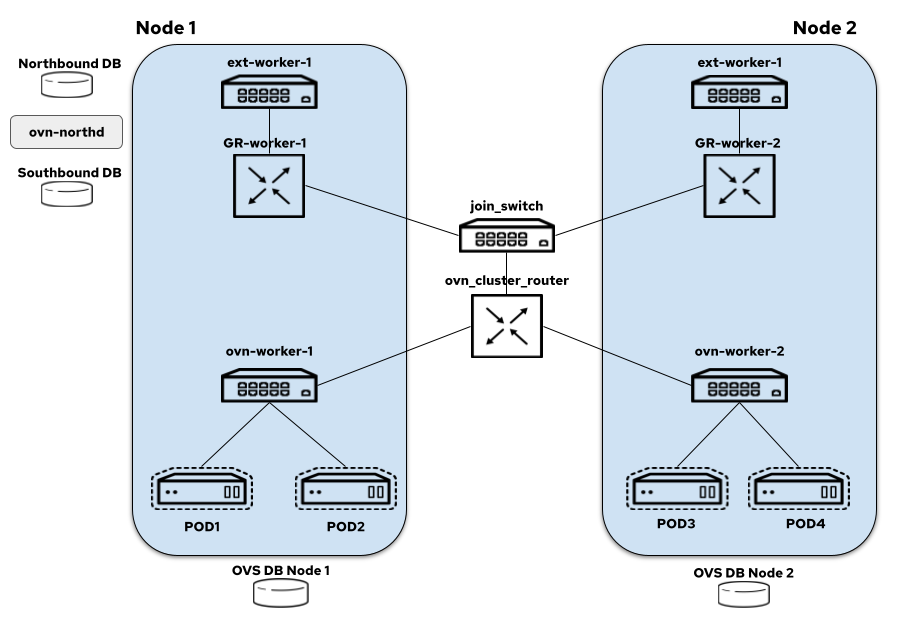
On each node we have:
- node-local-switch: all the logical switch ports for the pods created on a node are bound to this switch and it also hosts load balancers that take care of DNAT-ing the service traffic
- distributed-ovn-cluster-router: it's responsible for tunnelling overlay traffic between the nodes and also routing traffic between the node switches and gateway router's
- distributed-join-switch: connects the ovn-cluster-router to the gateway routers
- node-local-gateway-router: it's responsible for north-south traffic routing and connects the join switch to the external switch and it also hosts load balancers that take care of DNAT-ing the service traffic
- node-local-external-switch: connects the gateway router to the external bridge
OVN-Kubernetes Network Topology - Distributed (Interconnect) (DEFAULT)¶
The interconnect architecture in OVN-K looks like this today (we assume each node is in a zone of their own):
+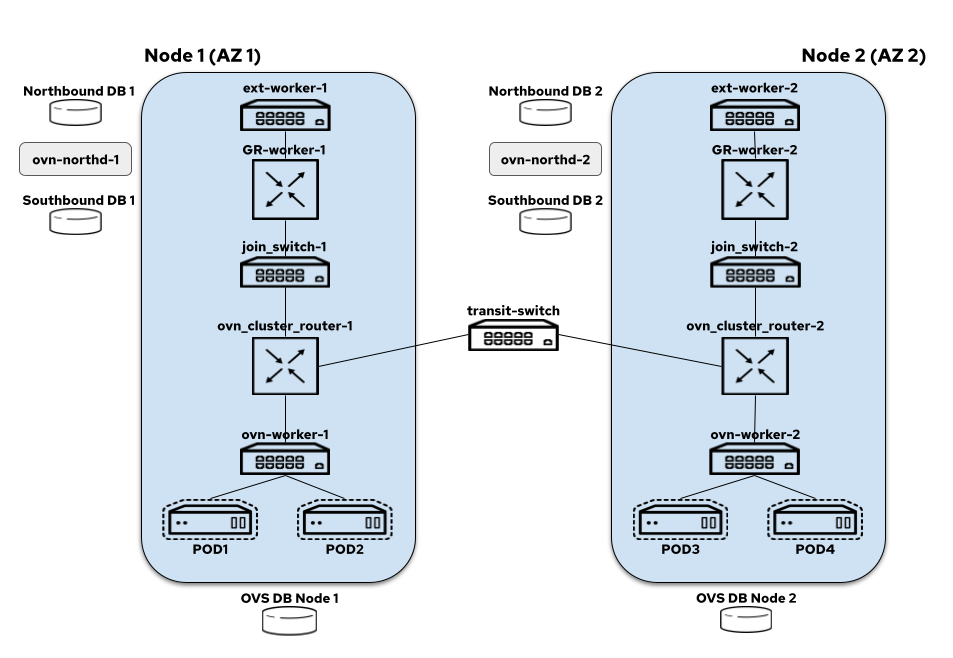
On each node we have:
- node-local-switch: all the logical switch ports for the pods created on a node are bound to this switch and it also hosts load balancers that take care of DNAT-ing the service traffic
- distributed-ovn-cluster-router: it's responsible for tunnelling overlay traffic between the nodes and also routing traffic between the node switches and gateway router's (note that if its one node per zone this behaves like a local router since there is no need for a distributed setup; if there are multiple nodes in the same zone, then it uses GENEVE tunnel for overlay traffic)
- distributed-join-switch: connects the ovn-cluster-router to the gateway routers (note that if its one node per zone this behaves like local switch since there is no need for a distributed setup; if there are multiple nodes in the same zone, then its distributed and connects cross more than one gateway router)
- node-local-gateway-router: it's responsible for north-south traffic routing and connects the join switch to the external switch and it also hosts load balancers that take care of DNAT-ing the service traffic
- node-local-external-switch: connects the gateway router to the external bridge
- transit-switch: This is the shiny new component coming in for IC. It is distributed across the nodes in the cluster and is responsible for routing traffic between the different zones.
FIXME: This page is lazily written, there is so much more to do here.